Gene Flow and Migration
Gene flow refers to the movement of genetic material within or between populations. It’s the process by which alleles (different versions of a gene) are shared, increasing genetic diversity. The result of gene flow is the alteration of allele frequencies in the recipient population. It can occur due to the movement of individuals carrying new alleles or through the dispersal of reproductive material like seeds or pollen. Gene flow can prevent populations from diverging too much genetically, helping maintain a species’ cohesion. Migration is the movement of individuals from one place to another. In a biological context, it often describes the seasonal movement of animals to and from breeding or feeding areas. When individuals migrate to a new population and breed, their genes become incorporated into the new gene pool, leading to gene flow. However, not all migration results in gene flow if, for instance, the newcomers don’t breed or don’t survive long enough to reproduce. Migration rate (Nm ) can be measured using the following equation: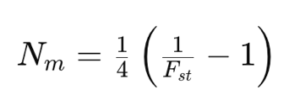
- Choose a small, isolated population (e.g., an island species, or a conservation-reliant species in a zoo) and think about how genetic drift might affect its genetic diversity over multiple generations. Discuss potential scenarios where genetic drift could either lead to the fixation of deleterious alleles or possibly aid in rapid adaptation to new environmental pressures.
- Evaluate the role of gene flow in counteracting the effects of genetic drift and selection in a fragmented habitat (e.g., a species living in an urbanized area e.g. rats in New York City or a species with habitat divided by human activity like roads or agriculture for e.g. deer in rural Massachusetts). What are the potential barriers to gene flow in this scenario, and how might they affect the population’s genetic structure? Propose practical interventions or habitat management strategies that could enhance gene flow and thus genetic diversity.
Media Attributions
- Migration rate

